1.
Write a program which prints information on the screen when variables
a and b fulfills the condition \(a \in (-\infty,0) \cup (10,+\infty)\) and
\(b \in (0,+\infty)\). Check if the
following code is working correctly and apply modifications if
necessary:
2.
Write a program which generates random 2D points. The points should
lay inside a rectangle shown on the figure. Keep on generating the
points until there will be \(N\) points
laying inside a circle placed inside the rectangle. Coordinates of the
rectangle and the circle should be hardcoded (do not read them from the
keyboard) and value of \(N\) should be
read from the keyboard. Use function rand for generating
the pseudorandom numbers. The function returns a pseudorandom integer in
the range 0 to RAND_MAX. In order to get
values in the range \((v_{min},
v_{max})\) use a scaling formula:
Pseudorandom numbers means that every time the generator is started
it will produce the same series of numbers. To improve that behavior
every time the generator is started it should initialized with different
value. It can be done with function srand which is called
once at the begining of a program:
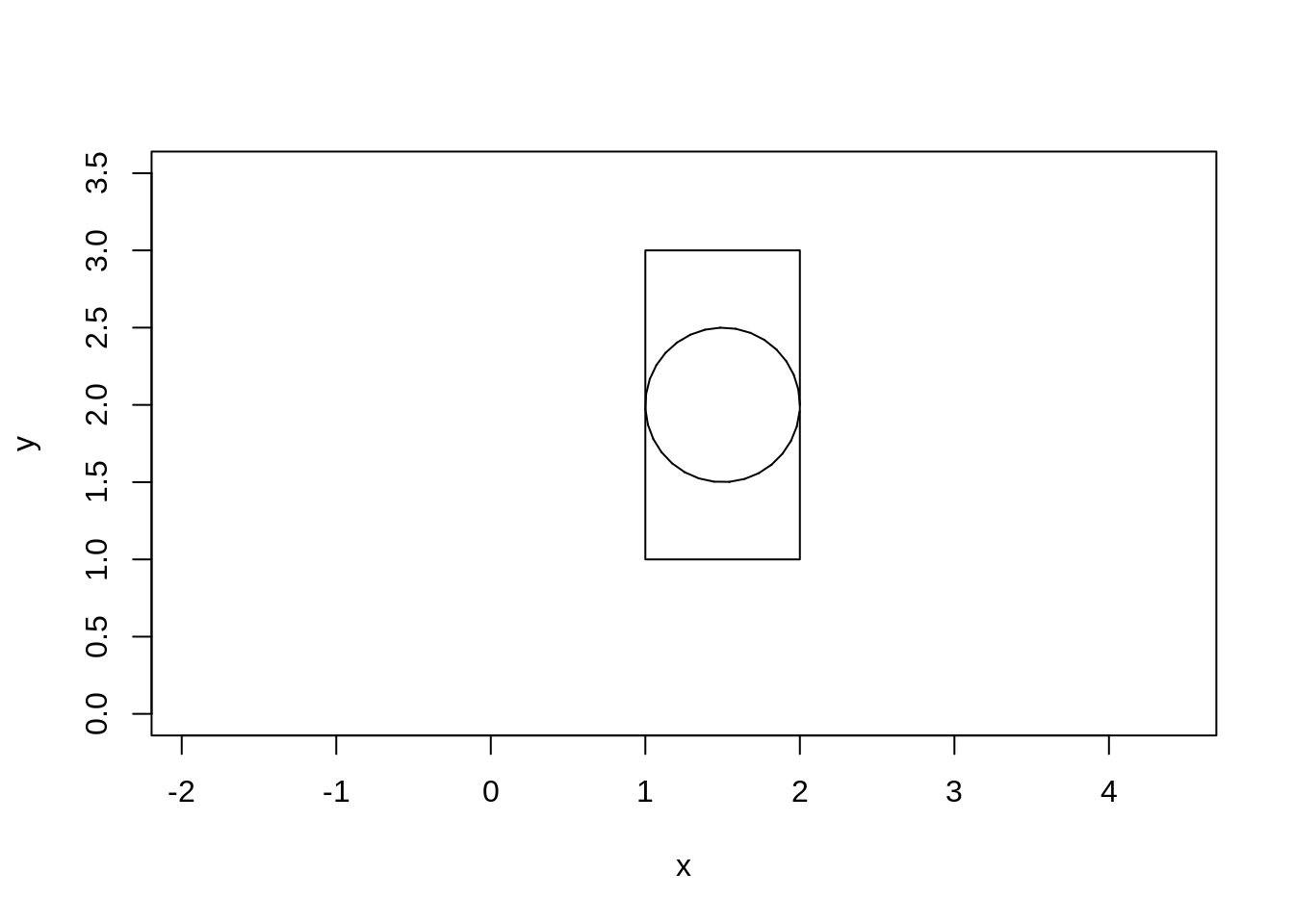
Execute the program for \(N\) = 7.
3.
Modify the program above in such a way that the coordinates of the points will be written to a file. Coordinates of the points laying inside the circle and outside the circle should be written in different columns. Writing data to the file can be done in the following way:
FILE *f; // declaration of a pointer to a file
f = fopen("data.dat", "wt"); // open the file with a name "data.dat"
// w - write
// r - read
// a - append
// t - text file
// b - binary file
if (f == NULL)
{
printf("Error opening a file.\n");
exit(-1); // exit the program
}
fprintf(f, "write to the file"); // here place the code to write your data
fclose(f); // close the fileShow the results using the point graph from Excel. Use different color for points laying inside the circle. Do this for \(N \in \{7,50,500 \}\).